
301 redirects help protect your website during an upgrade, redesign, or move. While they are really easy to implement, many website owners and developers forget about them and in the process, this derails SEO efforts and can completely wipe away ranking in search.
I’ll be honest, I didn’t think much about 301 redirects until recently. Creating and managing 301 redirects have been a core part of our website design and development projects and we have to do items listed for these within each project plan.
But lately, I’ve been seeing more and more questions in social media, email inquiries, and my Clarity.fm calls where website owners and bloggers have had major issues because no one considered or created 301 redirects when websites and blogs were redesigned or updated.
Today I had a call with the lovely Ivy and this was once again a problem. The sad part is that Ivy is a blogger and she had both WordPress developers and SEO consultants helping her, yet neither had a great handle on 301 redirects. They also failed to educate her on the importance of them, which really makes me angry.
After my call with Ivy I decided a blog post about 301 redirects is needed, so I’d like to do a quick recap on what 301 redirects are and why they are important.
What is a 301 Redirect?
If you need to change the URL of a page as it is shown in search engine results, Google recommends that you use a server-side 301 redirect. This is the best way to ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct page.
A 301 redirect is a status code that instructs search engines that a page/post has permanently moved to a new location. It asks the search engines to transfer prior SEO history to the new piece of content and at the same time it pushes website traffic to this new location.
When to Use a 301 Redirect
- You’ve moved your site to a new domain and you want to make sure both traffic and SEO history is routed to the new destination.
- You’ve changed a URL (page, post, product, category, etc.) and you want your existing PageRank* to transfer to the new URL.
- You’ve changed a URL and you want your traffic to the old URL rerouted to the new URL.
- You’re merging two websites and want to make sure that links to outdated URLs are redirected to the correct pages.
*Not sure what PageRank is? It’s simply a number from 0-10 which is assigned by Google. This number is an indication of how good your overall SEO is for a given piece of content. PageRank is a minor part of Google’s algorithm and is changed only a few times a year. Google would display this data for website owners in past years, but the visibility of it was taken away earlier this year. While it still exists, we cannot see our PageRank value.
Setting Up 301 Redirects
There are multiple ways to set up 301 redirects. Some are geared towards developers, while others are more user friendly and perfect for end users. There are the three methods we tend to use and recommend:
.htaccess File
To implement a 301 redirect for websites that are hosted on servers running Apache, you’ll need access to your server’s .htaccess file. For non-programmers, this can be a bit scary. While my coding team effortlessly manages .htaccess files, they scare me beyond words.

htaccess file 301 redirect example
Redirection Plugin for WordPress
If you are using WordPress, you can also use a plugin like Redirection to set up 301 redirects right from within your dashboard. This plugin is very intuitive and is easy enough for any website owner or blogger to use.
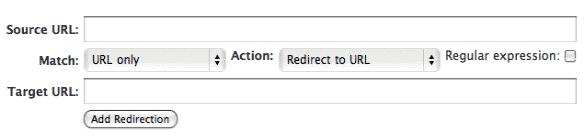
Redirection 301 Redirect Example
Final Comments
301 redirects are very important to SEO and the usability of your site. They not only pass PageRank and your SEO history, they also make sure users are not landing on 404 pages and dead ends.
You don’t have to be intimidated by 301 redirects. You just need to take the time to create and load them anytime you delete content, move content, or restructure your website architecture.
Web Savvy Marketing
TwitterYoutubeFacebookLinkedinGoogle +